React Web 动画的 5 种创建方式,每一种都不简单
原文:React Animations in Depth by Nader Dabit
在 Tweet 得到很多大佬关于 React Web 动画 不错的的回应,于是决定在这里分享给大家。
以下便是本文要分享的创建 React 动画 的几种方式:
- CSS animation
- JS Style
- React Motion
- Animated
- Velocity React
CSS animation
给元素添加 class 是最简单,最常见的书写方式,如果你的 app 正在使用 CSS,那么这将是你最愉快的选择。
赞同者:
- 我们只需修改 opacity 和 transform 这样的属性,就可构建基本的动画;
- 在组件中,我们可以非常容易地通过 state 去更新这些值;
反对者:
- 这种方式并 不跨平台,在 React Native 中就不适用;
- 对于较复杂的动画,这种方式难以控制;
接下来,我们通过一个简单的 demo 来体验一下这种创建方式:当 input focus 的时候,我们增加它的宽度。
首先,我们创建两个 input 要用到的 class:
.input {
width: 150px;
padding: 10px;
font-size: 20px;
border: none;
border-radius: 4px;
background-color: #dddddd;
transition: width 0.35s linear;
outline: none;
}
.input-focused {
width: 240px;
}一个是它原始的样式,一个是它 focus 后的样式。
下面,我们就开始书写我们的 React 组件。
class App extends Component {
state = {
focused: false,
};
componentDidMount() {
this._input.addEventListener("focus", this.focus);
this._input.addEventListener("blur", this.focus);
}
focus = () => {
this.setState(prevState => ({
focused: !prevState.focused,
}));
};
render() {
return (
<div className="App">
<div className="container">
<input
ref={input => (this._input = input)}
className={["input", this.state.focused && "input-focused"].join(
" ",
)}
/>
</div>
</div>
);
}
}- 我们有一个 focused 的
state,初始值为 false,我们通过更新该值来创建我们的动画; - 在
componentDidMount时,我们添加两个监听器,一个 focus,一个 blur,指定的回调函数都是 focus; focus方法会获取之前 focused 的值,并负责切换该值;- 在
render中,我们通过 state 来改变 input 的 classNames,从而实现我们的动画;
JS Style
JavaScript styles 跟 CSS 中的 class 类似。
赞同者:
- 跟 CSS 动画一样,且它的表现更为清晰,且可以不必依赖 CSS;
反对者:
- 跟 CSS 动画一样,不跨平台,且动画一旦复杂,也难以控制;
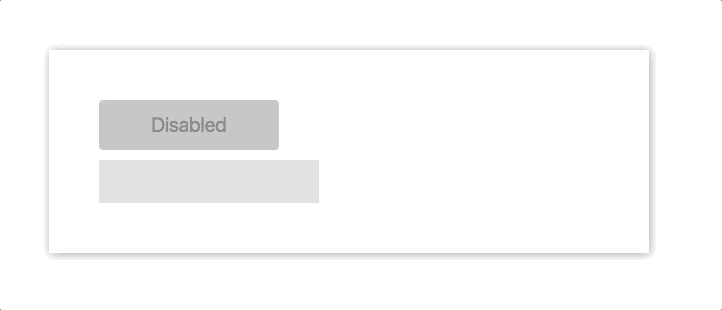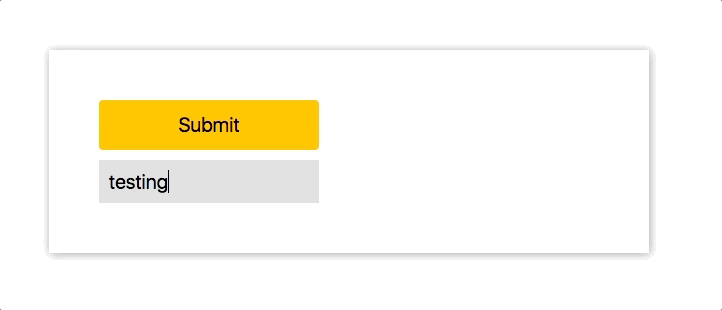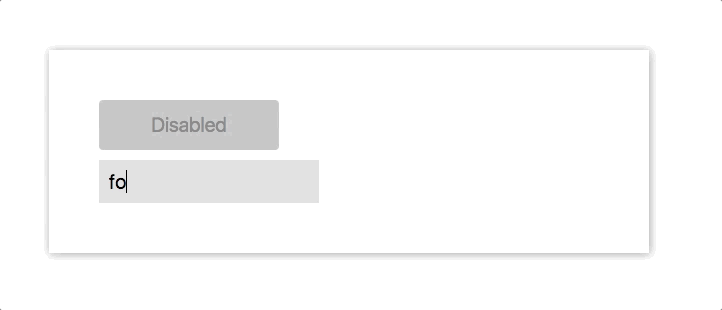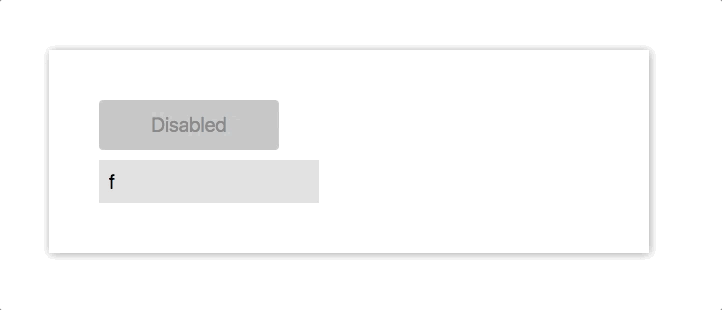
在下面的 demo 中,我们将创建一个 input,当用户输入时,我们将一个 button 从 disable 转变为 enable。
class App extends Component {
state = {
disabled: true,
};
onChange = e => {
const length = e.target.value.length;
if (length > 0) {
this.setState({ disabled: false });
} else {
this.setState({ disabled: true });
}
};
render() {
const { disabled } = this.state;
const label = disabled ? "Disabled" : "Submit";
return (
<div style={styles.App}>
<input style={styles.input} onChange={this.onChange} />
<button
style={Object.assign(
{},
styles.button,
!this.state.disabled && styles.buttonEnabled,
)}
disabled={disabled}>
{label}
</button>
</div>
);
}
}
const styles = {
App: {
display: "flex",
justifyContent: "left",
},
input: {
marginRight: 10,
padding: 10,
width: 190,
fontSize: 20,
border: "none",
backgroundColor: "#ddd",
outline: "none",
},
button: {
width: 90,
height: 43,
fontSize: 17,
border: "none",
borderRadius: 4,
transition: ".25s all",
cursor: "pointer",
},
buttonEnabled: {
width: 120,
backgroundColor: "#ffc107",
},
};- 我们有一个 disabled 的
state,初始值为 true; onChange方法会获取用户的输入,当输入非空时,就切换 disabled 的值;- 根据 disabled 的值,确定是否将
buttonEnabled添加到 button 中;
React Motion
React Motion 是 Cheng Lou 书写的一个非常不错的开源项目。它的思想是可以对 Motion 组件进行简单的样式设置,然后你就可以在回调函数中通过这些值,享受动画带来的乐趣。
对于绝大多数的动画组件,我们往往不希望对动画属性(宽高、颜色等)的变化时间做硬编码处理,react-motion 提供的 spring 函数就是用来解决这一需求的,它可以逼真地模仿真实的物理效果,也就是我们常见的各类 缓动效果。
下面是一个简单的 demo:
<Motion style={{ x: spring(this.state.x) }}>
{({ x }) => <div style={{ transform: `translateX(${x}px)` }} />}
</Motion>这是官方提供的几个 demo,可谓是不看不知道,一看吓一跳。
赞同者:
- React Motion 可以在 React Web 中使用,也可以在 React Native 中使用,因为它 跨平台;
- 其中的 spring 概念最开始对我来说很陌生,然而上手之后,发现它真的很神奇,并且,它有很详细的 API;
反对者:
- 在某些情况下,他不如纯 CSS / JS 动画;
- 虽然它有不错的 API,容易上手,但也需要学习成本;
首先使用 yarn 或 npm 安装:
$ yarn add react-motion在下面的 demo 中,我们将创建一个 dropdown 菜单,当点击按钮时,下拉菜单友好展开。
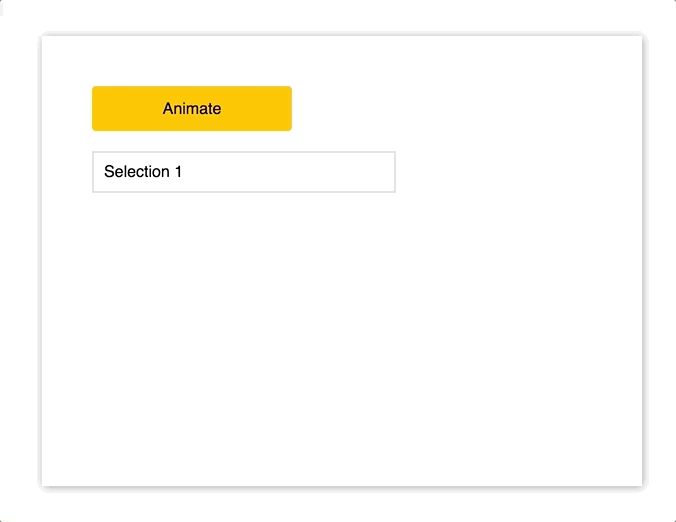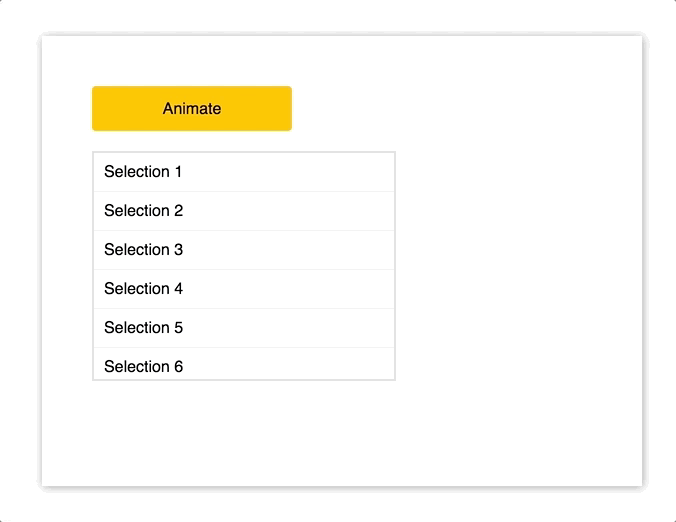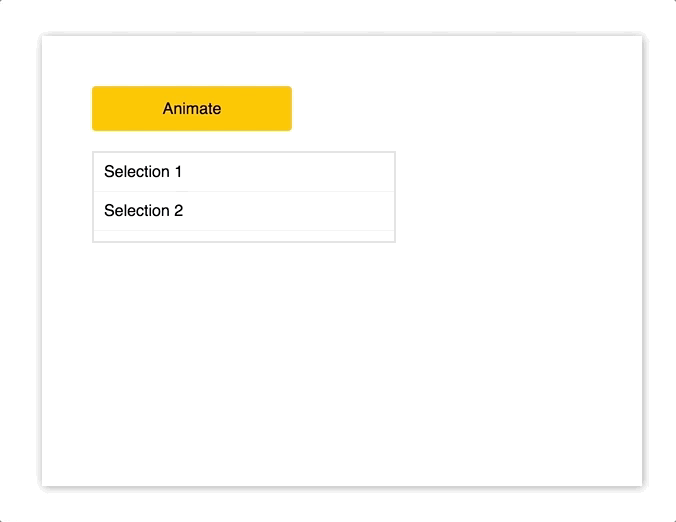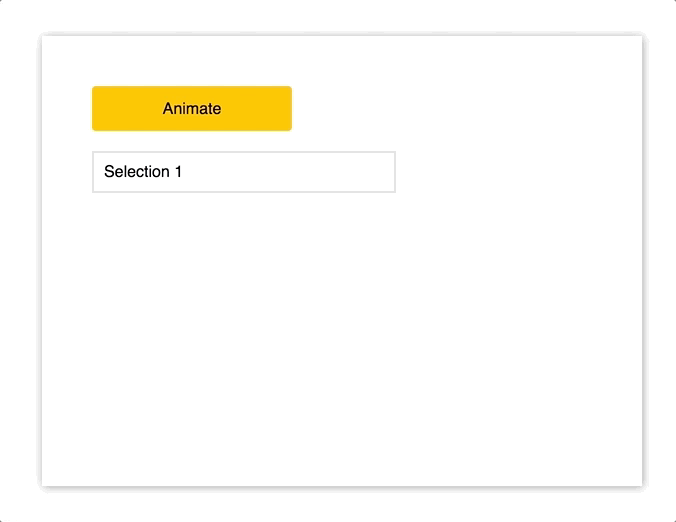
import { Motion, spring } from "react-motion";
class App extends Component {
state = {
height: 38,
};
animate = () => {
this.setState(state => ({ height: state.height === 233 ? 38 : 233 }));
};
render() {
return (
<div className="App">
<div style={styles.button} onClick={this.animate}>
Animate
</div>
<Motion style={{ height: spring(this.state.height) }}>
{({ height }) => (
<div style={Object.assign({}, styles.menu, { height })}>
<p style={styles.selection}>Selection 1</p>
<p style={styles.selection}>Selection 2</p>
<p style={styles.selection}>Selection 3</p>
<p style={styles.selection}>Selection 4</p>
<p style={styles.selection}>Selection 5</p>
<p style={styles.selection}>Selection 6</p>
</div>
)}
</Motion>
</div>
);
}
}
const styles = {
menu: {
marginTop: 20,
width: 300,
border: "2px solid #ddd",
overflow: "hidden",
},
button: {
display: "flex",
width: 200,
height: 45,
justifyContent: "center",
alignItems: "center",
border: "none",
borderRadius: 4,
backgroundColor: "#ffc107",
cursor: "pointer",
},
selection: {
margin: 0,
padding: 10,
borderBottom: "1px solid #ededed",
},
};- 我们从 react-motion 中 import
Motion和spring; - 我们有一个 height 的
state,初始值为 38,代表 menu 的高度; animate方法设置 menu 的 height,切换 height 的值;- 在
render中,我们使用 Motion 组件包装整个 p 标签列表,将 state.height 的当前值设为组件的 height,然后在组件的回调函数中使用该值作为整个下拉的高度; - 当按钮被点击时,我们通过
this.animate切换下拉的高度;
Animated
Animated 是基于 React Native 使用的同一个动画库建立起来的。
它背后的思想是创建 声明式动画,通过传递配置对象来控制动画。
赞同者:
- 跨平台,它在 React Native 中已经非常稳定,如果你在 React Native 中使用过,那么你将不用再重复学习;
- 其中的
interpolate是一个神奇的插值函数,我们将在下面看到;
反对者:
- 目前不是 100% 的稳定,在老的浏览器中的,存在前缀和性能的问题;
首先使用 yarn 或 npm 安装:
$ yarn add animated在下面的 demo 中,我们将模拟在提交表单成功后显示的动画 message。
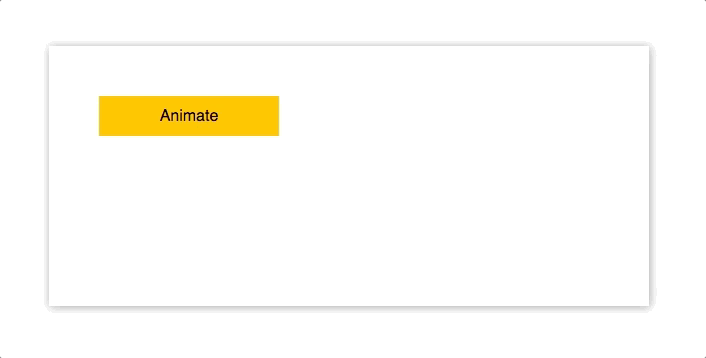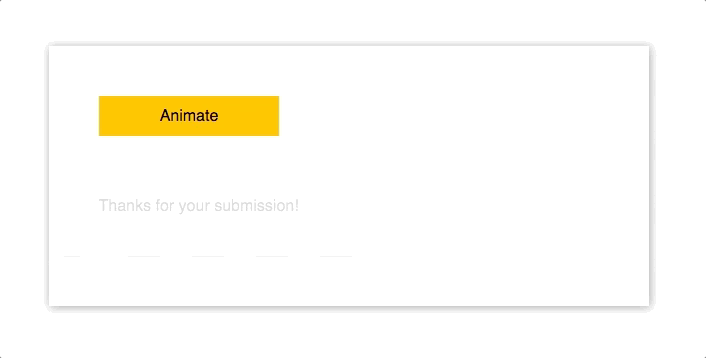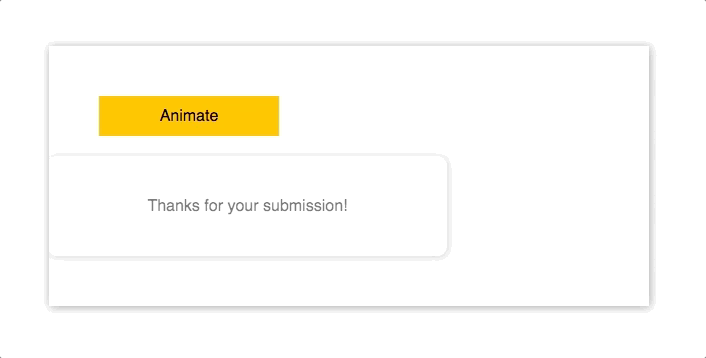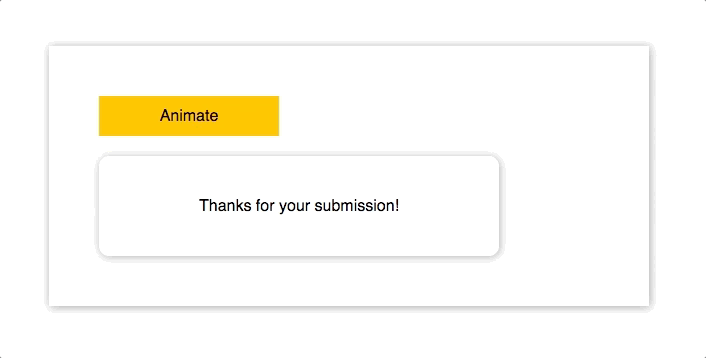
import Animated from "animated/lib/targets/react-dom";
import Easing from "animated/lib/Easing";
class AnimatedApp extends Component {
animatedValue = new Animated.Value(0);
animate = () => {
this.animatedValue.setValue(0);
Animated.timing(this.animatedValue, {
toValue: 1,
duration: 1000,
easing: Easing.elastic(1),
}).start();
};
render() {
const marginLeft = this.animatedValue.interpolate({
inputRange: [0, 1],
outputRange: [-120, 0],
});
return (
<div className="App">
<div style={styles.button} onClick={this.animate}>
Animate
</div>
<Animated.div
style={Object.assign({}, styles.box, {
opacity: this.animatedValue,
marginLeft,
})}>
<p>Thanks for your submission!</p>
</Animated.div>
</div>
);
}
}
const styles = {
button: {
display: "flex",
width: 125,
height: 50,
justifyContent: "center",
alignItems: "center",
border: "none",
borderRadius: 4,
backgroundColor: "#ffc107",
cursor: "pointer",
},
box: {
display: "inline-block",
marginTop: 10,
padding: "0.6rem 2rem",
fontSize: "0.8rem",
border: "1px #eee solid",
borderRadius: 4,
boxShadow: "0 2px 8px rgba(0,0,0,.2)",
},
};- 从 animated 中 import
Animated和Easing; - 用
new Animated.Value(0)创建一个值为 0 的类属性 - animatedValue; - 创建
animate方法,处理所有的动画,首先通过this.animatedValue.setValue(0)初始化动画值,实现的效果就是每次重新执行该动画,然后调用Animated.timing,animatedValue 作为第一个参数传递,配置对象作为第二个参数,一个设置最终动画值,一个设置持续时间,一个设置 缓动效果。 - 在
render中,我们用interpolate方法创建 marginLeft 对象,包含 inputRange 和 outputRange 数组,我们使用此对象作为 UI 中 message 的 style 属性; - 我们使用
Animated.div替代默认的 div; - 我们将 animatedValue 和 marginLeft 作为
Animated.div的 style 属性;
Velocity React
Velocity React 是基于已经存在的 Velocity 建立起来的。
赞同者:
- 上手容易,API 简单明了,相对其他库更易于掌握;
反对者:
- 有些不得不克服的问题,比如 componentDidMount 后动画并没有真正地起作用等;
- 不跨平台;
下面是一个简单的 demo:
<VelocityComponent
animation={{ opacity: this.state.showSubComponent ? 1 : 0 }}
duration={500}>
<MySubComponent />
</VelocityComponent>首先还是先用 yarn 或 npm 安装:
$ yarn add velocity-react在下面的 demo 中,我们将创建一个很酷的动画输入。
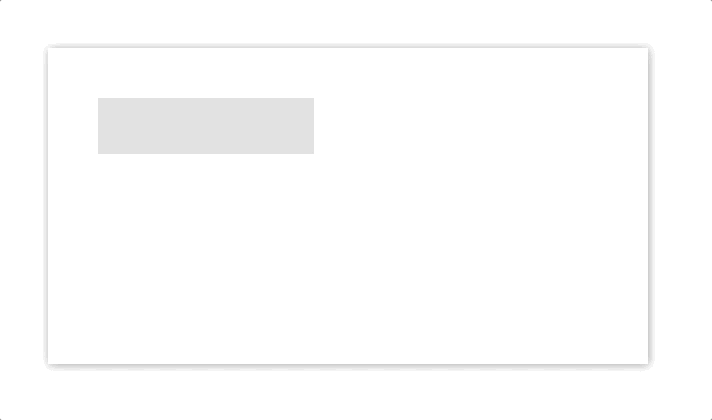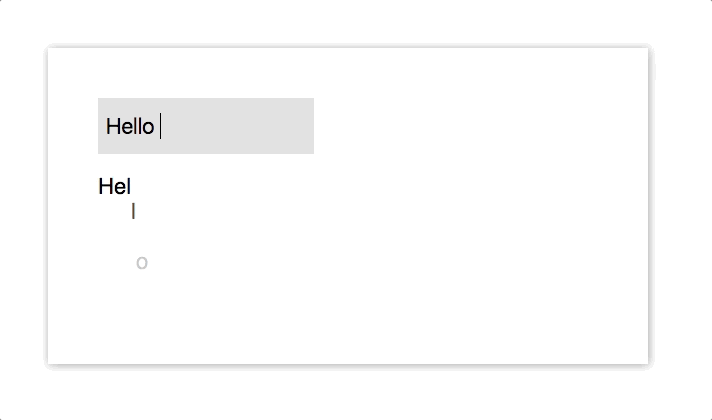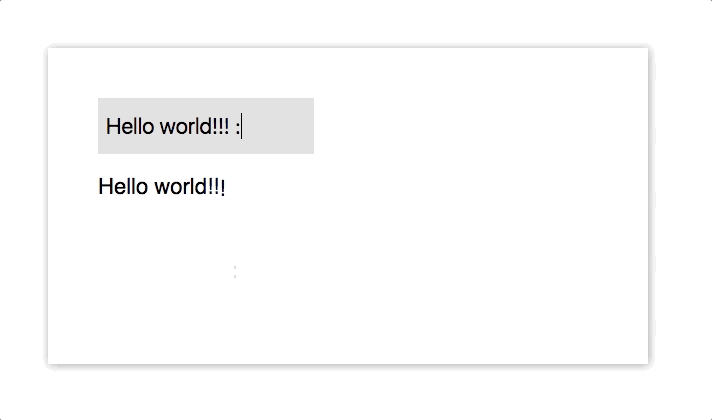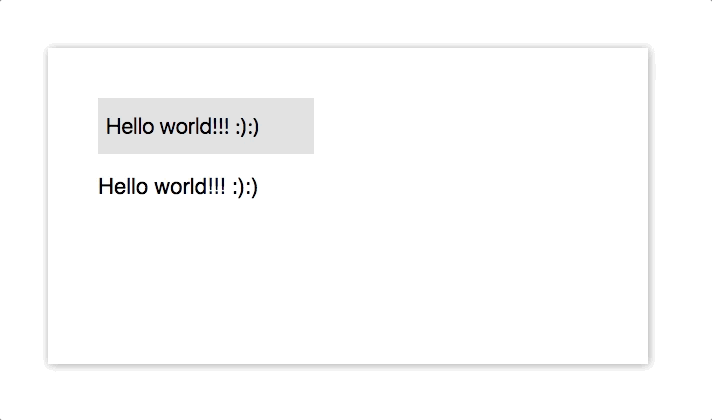
import { VelocityComponent } from "velocity-react";
const VelocityLetter = ({ letter }) => (
<VelocityComponent
runOnMount
animation={{ opacity: 1, marginTop: 0 }}
duration={500}>
<p style={styles.letter}>{letter}</p>
</VelocityComponent>
);
class VelocityApp extends Component {
state = {
letters: [],
};
onChange = e => {
const letters = e.target.value.split("");
const arr = [];
letters.forEach((l, i) => {
arr.push(<VelocityLetter letter={l} />);
});
this.setState({ letters: arr });
};
render() {
return (
<div className="App">
<div className="container">
<input onChange={this.onChange} style={styles.input} />
<div style={styles.letters}>{this.state.letters}</div>
</div>
</div>
);
}
}
const styles = {
input: {
marginBottom: 20,
padding: 8,
width: 200,
height: 40,
fontSize: 22,
backgroundColor: "#ddd",
border: "none",
outline: "none",
},
letters: {
display: "flex",
height: 140,
},
letter: {
marginTop: 100,
fontSize: 22,
whiteSpace: "pre",
opacity: 0,
},
};- 从 velocity-react 中 import
VelocityComponent; - 我们要创建一个可重复使用的组件来满足每个 letter 的动画;
- 在这个组件中,我们将 animation 的
opacity设为 1,marginTop设为 0,这些值代表着传入子组件的重写值,即当组件被创建时,组件的opacity会由初始的 0 变为 1,marginTop会由初始的 100 变为 0,我们还设置了 500 ms 的持续时间,最后值得一提的是runOnMount属性,它的意思是在组件挂载或创建完后执行该动画; - 其中的
onChange方法会获取用户的每次输入,并创建一个由 VelocityLetter 组成的新数组; - 在
render中,我们就使用该数组在 UI 中渲染 letters;
总结
总的来说,基本的动画,我会选择 JS style,复杂的动画,我更偏向 React Motion,而对于 React Native,我还是坚持使用 Animated,一旦 Animated 成熟,在 Web 中可能也会投入使用,目前,我很享受 React Motion。